How Is Photosynthesis Related To Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Concentrations And Climate Change
The alarming rate of carbon dioxide flowing into our atmosphere is affecting institute life in interesting ways – but mayhap not in the way yous'd expect.
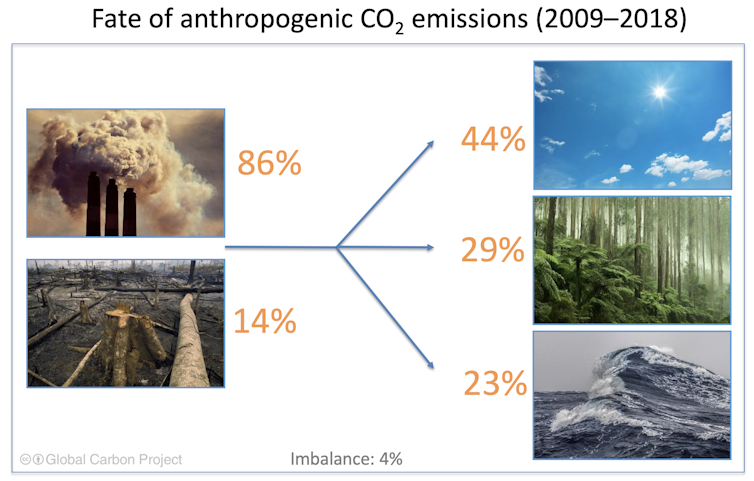
Despite large losses of vegetation to land clearing, drought and wildfires, carbon dioxide is captivated and stored in vegetation and soils at a growing charge per unit.
This is chosen the "land carbon sink", a term describing how vegetation and soils around the world blot more than carbon dioxide from photosynthesis than they release. And over the by 50 years, the sink (the difference between uptake and release of carbon dioxide past those plants) has been increasing, absorbing at to the lowest degree a quarter of human being emissions in an average twelvemonth.
The sink is getting larger because of a rapid increase in institute photosynthesis, and our new research shows rising carbon dioxide concentrations largely bulldoze this increase.
So, to put it but, humans are producing more carbon dioxide. This carbon dioxide is causing more institute growth, and a higher capacity to suck up carbon dioxide. This process is called the "carbon dioxide fecundation effect" – a miracle when carbon emissions boost photosynthesis and, in turn, plant growth.
What nosotros didn't know until our study is just how much the carbon dioxide fertilisation outcome contributes to the increase in global photosynthesis on country.
But don't get confused, our discovery doesn't mean emitting carbon dioxide is a good thing and we should pump out more carbon dioxide, or that land-based ecosystems are removing more carbon dioxide emissions than we previously thought (nosotros already know how much this is from scientific measurements).
And it definitely doesn't hateful hateful we should, as climate sceptics have washed, utilize the concept of carbon dioxide fertilisation to downplay the severity of climate modify.
Baca juga: How to pattern a woods fit to heal the planet
Rather, our findings provide a new and clearer caption of what causes vegetation around the earth to blot more carbon than it releases.
What's more than, nosotros highlight the capacity of vegetation to absorb a proportion of human emissions, slowing the charge per unit of climate change. This underscores the urgency to protect and restore terrestrial ecosystems like forests, savannas and grasslands and secure their carbon stocks.
And while more carbon dioxide in the temper does let landscapes to absorb more carbon dioxide, nearly half (44%) of our emissions remain in the atmosphere.
More carbon dioxide makes plants more efficient
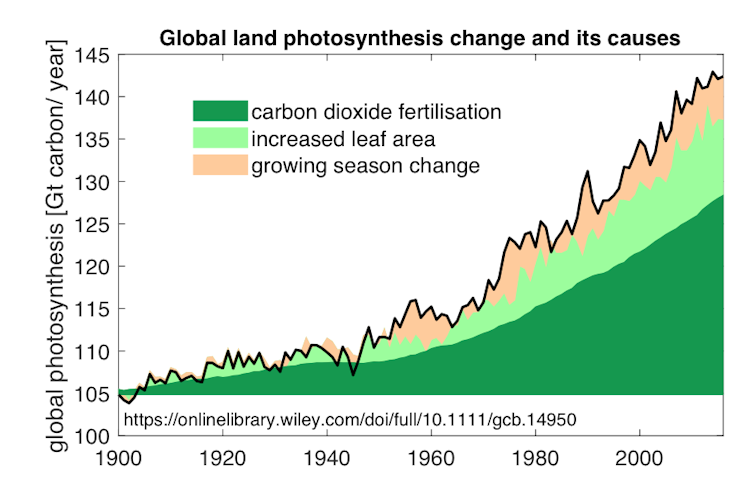
Since the beginning of the last century, photosynthesis on a global scale has increased in nigh abiding proportion to the ascension in atmospheric carbon dioxide. Both are now around xxx% college than in the 19th century, before industrialisation began to generate significant emissions.
Carbon dioxide fertilisation is responsible for at least 80% of this increase in photosynthesis. Almost of the rest is attributed to a longer growing season in the quickly warming boreal forest and Arctic.

And then how does more than carbon dioxide pb to more establish growth anyhow?
Higher concentrations of carbon dioxide make plants more productive because photosynthesis relies on using the sun's free energy to synthesise saccharide out of carbon dioxide and h2o. Plants and ecosystems use the sugar both every bit an free energy source and as the basic building block for growth.
When the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air outside a plant leafage goes up, it can exist taken upward faster, super-charging the charge per unit of photosynthesis.
Baca juga: CO₂ levels and climatic change: is there really a controversy?
More carbon dioxide also means h2o savings for plants. More carbon dioxide available means pores on the surface of establish leaves regulating evaporation (called the stomata) can close slightly. They still absorb the same amount or more of carbon dioxide, but lose less water.
The resulting water savings can benefit vegetation in semi-arid landscapes that dominate much of Australia.
We saw this happen in a 2013 report, which analysed satellite data measuring changes in the overall greenness of Commonwealth of australia. Information technology showed more leaf expanse in places where the amount of rain hadn't inverse over time. This suggests h2o efficiency of plants increases in a carbon dioxide-richer world.
Young forests aid to capture carbon dioxide
In other research published recently, we mapped the carbon uptake of forests of different ages around the earth. We showed forests regrowing on abased agricultural state occupy a larger area, and draw downwardly fifty-fifty more carbon dioxide than old-growth forests, globally. Only why?
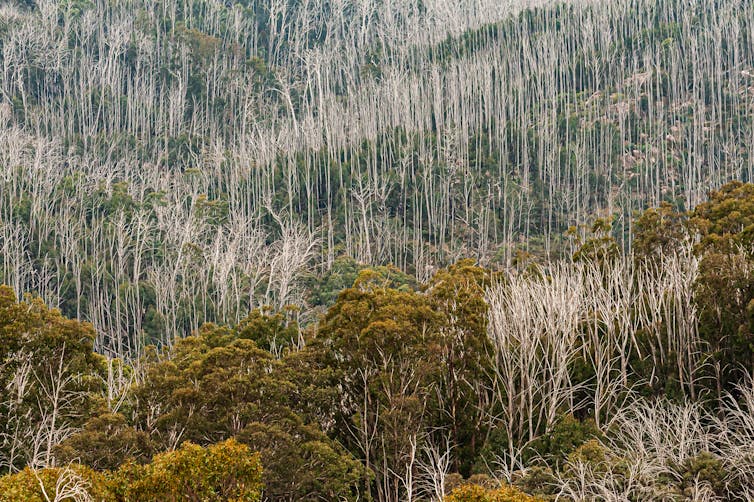

In a mature forest, the death of old trees balances the amount of new forest grown each year. The quondam trees lose their wood to the soil and, eventually, to the atmosphere through decomposition.
A regrowing forest, on the other hand, is still accumulating woods, and that means information technology can human activity as a considerable sink for carbon until tree mortality and decomposition grab up with the charge per unit of growth.
Baca juga: Forest thinning is controversial, only it shouldn't be ruled out for managing bushfires
This age effect is superimposed on the carbon dioxide fertilisation outcome, making young forests potentially very strong sinks.
In fact, globally, we found such regrowing forests are responsible for effectually 60% of the total carbon dioxide removal past forests overall. Their expansion by reforestation should be encouraged.
Forests are important to gild for so many reasons – biodiversity, mental wellness, recreation, water resources. By absorbing emissions they are also office of our available arsenal to combat climate change. Information technology's vital we protect them.
Source: https://theconversation.com/yes-more-carbon-dioxide-in-the-atmosphere-helps-plants-grow-but-its-no-excuse-to-downplay-climate-change-130603#:~:text=Higher%20concentrations%20of%20carbon%20dioxide,basic%20building%20block%20for%20growth.
Posted by: marinohaductincer.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Is Photosynthesis Related To Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Concentrations And Climate Change"
Post a Comment